What Is a Lipoma?
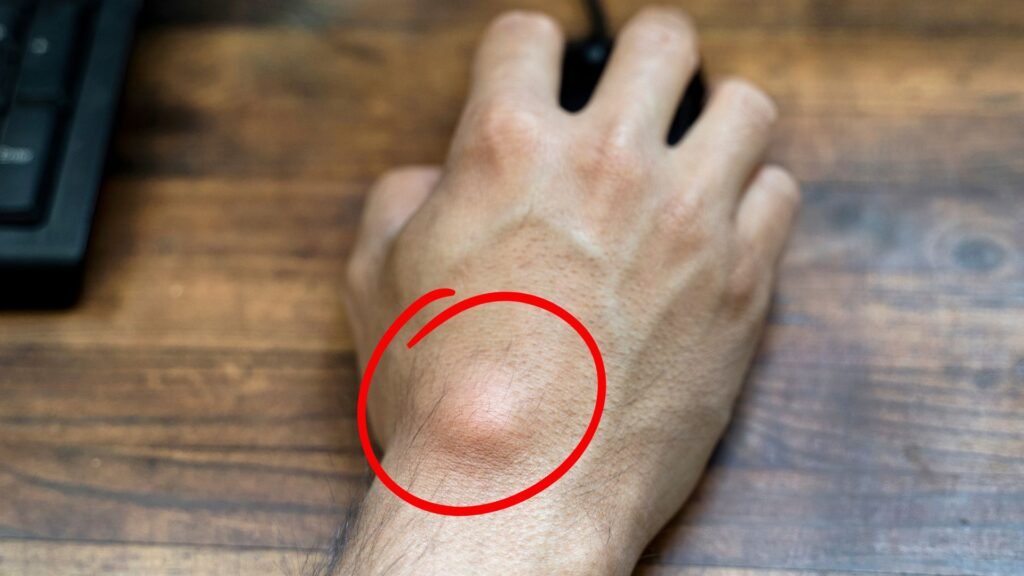
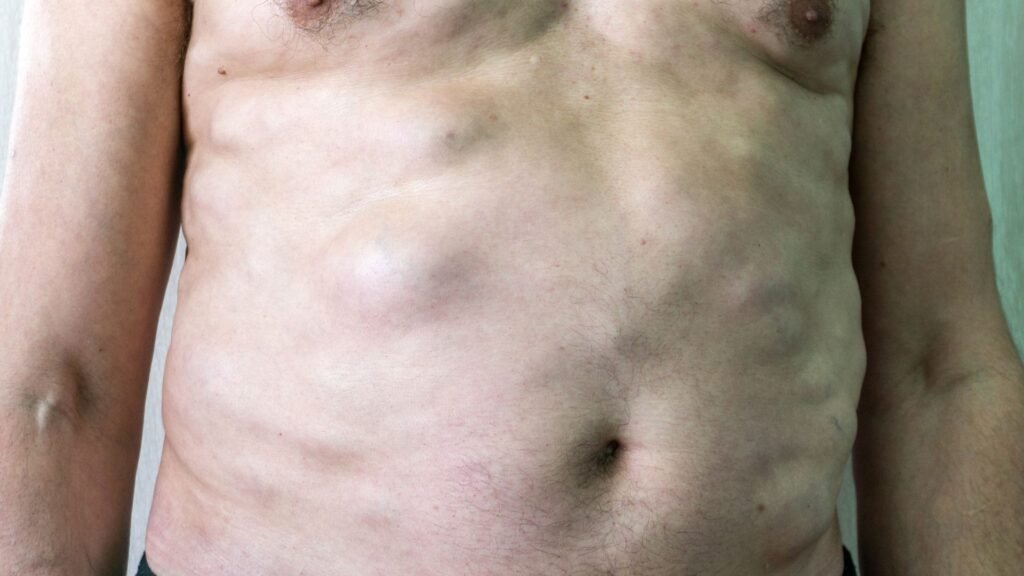
A lipoma is a benign, noncancerous tumor composed of fatty tissue that most often develops just beneath the skin. These soft, movable, round or oval-shaped lumps are usually painless and slow-growing, commonly found on the trunk, shoulders, neck, and arms. While lipomas are not dangerous, their appearance or discomfort may prompt many to seek medical advice.
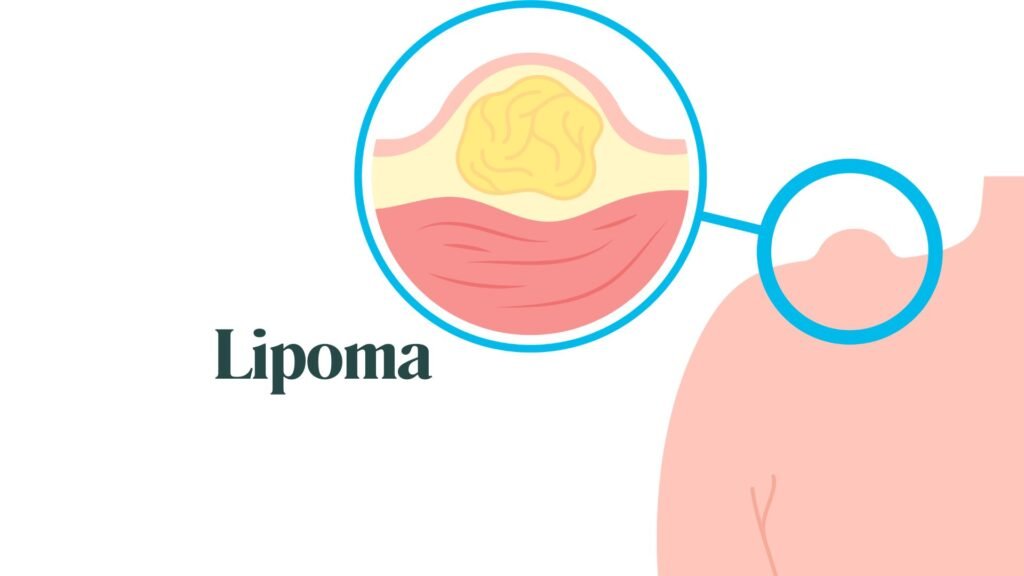
Lipoma Symptoms
- Soft, rubbery lump under the skin that moves easily to touch
- Usually painless, but may cause discomfort if pressing on nerves or near a joint
- Size varies from less than 1 cm to several centimeters in diameter
- Slow-growing in nature
- Most commonly found on the back, neck, arms, shoulders, and thighs
- Generally not associated with redness or changes in the skin above
- In rare cases, lipomas may become painful or inflamed, especially in certain conditions like Dercum’s disease
Causes and Risk Factors of Lipoma
- Exact causes remain unknown, but lipoma development is often linked to genetic factors
- Family history of lipoma increases risk (familial multiple lipomatosis)
- Associated medical syndromes: Dercum’s disease (adiposis dolorosa), Gardner’s syndrome, Madelung’s disease, Cowden syndrome
- Occasional occurrence after blunt injury or trauma to a particular area
- Risk increases between the ages of 40 and 60, but lipomas can develop at any age and may occur in both men and women
- Other risk factors: obesity, alcohol use disorder, certain metabolic conditions
Lipoma Diagnosis
Doctors usually diagnose a lipoma based on a physical exam. If the lump is large, painful, or growing rapidly, further tests like ultrasound, MRI, or biopsy may be performed to rule out cancerous tumors such as liposarcoma.
Lipoma Treatment Options
While most lipomas do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns, several effective procedures are available:
- Surgical Lipoma Removal: The most common approach, involving excision of the entire lump under local anesthesia. This method ensures complete removal and minimal recurrence risk.
- Liposuction for Lipoma: Fatty tissue is suctioned out through a small incision, suitable for larger or multiple lipomas. May not guarantee full removal if some tissue remains.
- Steroid Injection: Can shrink the lipoma by reducing its size, although it may not remove it completely.
- Injection Lipolysis for Lipoma: Involves injecting substances to dissolve fat; results can vary and this method is less common.
- Laser Treatment for Lipoma: Minimally invasive option emerging as an alternative for some types of lipoma.
- Non-Surgical Lipoma Treatments: Generally limited; most home remedies lack clinical evidence but are sometimes explored for smaller, superficial lumps.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if the lump is:
- Painful or rapidly increasing in size
- Associated with changes in the skin or becomes hard and immovable
- Causing cosmetic concerns or interfering with movement
- Not diagnosed previously or if there is any concern about cancer
FAQs About Lipoma and Its Treatment
- Is a lipoma dangerous?
- Lipomas are benign and rarely become cancerous, but all unusual growths should be evaluated by a doctor.
- What is lipoma excision recovery like? Most people recover quickly, with minimal scarring and low recurrence rates after surgery.
- Can lipomas be prevented? There’s no known way to prevent lipomas, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle and monitoring for changes can help.
- What about home remedies for lipoma? While many seek natural options, there’s little scientific support for effective home remedies.
Conclusion
For personalized advice and expert care, reach out to Divine Healthcare for a free consultation on lipoma removal. Our team of 30+ specialized lipoma doctors is ready to help you choose the best treatment options and guide you every step of the way.